Langkah 1: Hubungkan peralatan
- Hubungkan Router1 interface Serial 0/0/0 untuk antarmuka Router2 Serial 0/0/0 menggunakan kabel serial
- Hubungkan Router2 interface Serial 0/0/1 untuk antarmuka Router3 Serial 0/0/1 menggunakan kabel serial.
- Hubungkan Router1 untuk Router3 dengan kabel serial seperti ditunjukkan dalam diagram dan tabel.
- Hubungkan Fa0 di / 0 interface setiap router ke Fa0 / 1 antarmuka pada saklar yang sesuai.
- Hubungkan PC dengan kabel konsol untuk melakukan konfigurasi pada router dan switch.
- Hubungkan masing-masing PC host untuk Fa0 pada / 2 antarmuka pada saklar dengan menggunakan suatu lurus-melalui kabel.
Langkah 2: Lakukan konfigurasi dasar pada Router1
Lakukan konfigurasi dasar tentang Router1 dengan nama host, interface, konsol, Telnet, dan diistimewakan password sesuai dengan diagram tabel. Gunakan RIP sebagai protokol routing, dan mengiklankan terlampir jaringan. Simpan konfigurasi.
Langkah 3: Konfigurasi router lainnya
Lakukan konfigurasi dasar yang sama pada Router2 dan Router3 dengan nama host, interface, konsol, Telnet, dan password istimewa sesuai dengan diagram tabel. Gunakan RIP sebagai protokol routing, dan mengiklankan terpasang jaringan. Simpan konfigurasi.
Langkah 4: Konfigurasi host dengan alamat IP yang tepat, subnet mask, dan gateway default
Mengkonfigurasi setiap host dengan alamat IP yang tepat, subnet mask, dan gateway default.
Dari konfigurasi yang diberikan, apa yang akan menjadi alamat IP subnetwork berikutnya tersedia di 172.30.0.0 jaringan?
Dari konfigurasi yang diberikan, apa yang akan menjadi alamat IP subnetwork berikutnya tersedia di 172.30.0.0 jaringan?
Jawaban : 172.30.3.0
Jika Anda diperlukan untuk mengakomodasi LAN tambahan dengan 60 host, apa masker yang akan Anda gunakan untuk itu subnetwork?
Jawaban : / 26 (atau 255.255.255.192)
Langkah 5: Pastikan bahwa jaringan berfungsi
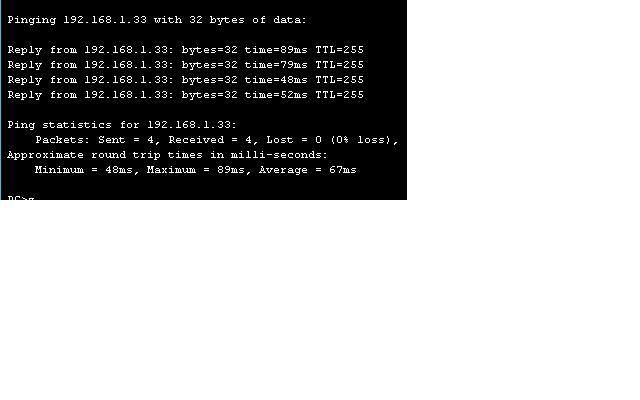
a. Dari setiap host, ping gateway default.
a. Dari setiap host, ping gateway default.
Apakah ping dari Host1 berhasil? Ya
Apakah ping dari host2 berhasil? Ya
Apakah ping dari sukses Host3? Ya
Jika jawabannya tidak untuk pertanyaan, memecahkan masalah konfigurasi router dan host
untuk menemukan kesalahan. Ping lagi sampai mereka berhasil.
b. Untuk setiap router, melihat status interface. Utama # show interface ip singkat
Branch1 # show ip interface singkat
Branch2 # show ip interface singkat
b. Untuk setiap router, melihat status interface. Utama # show interface ip singkat
Branch1 # show ip interface singkat
Branch2 # show ip interface singkat
Apakah status dan protokol terdaftar sebagai up untuk semua interface yang aktif?
Jawaban : Ya.
Jika jawabannya tidak, memecahkan masalah konfigurasi router untuk menemukan kesalahan. Periksa kembali sampai status dan protokol yang up.
Langkah 6: Memeriksa tabel routing
Dari topologi jaringan, berapa banyak jalan harus setiap laporan router dalam tabel routing untuk memiliki lengkap gambar jaringan?
Jawaban : 6 Pada setiap router, melihat tabel routing. Perintah dan output untuk Main ditunjukkan berikut ini:
Masalah apa yang Anda lihat dalam tabel routing?
Jawaban : Setiap router hanya melaporkan dua jaringan terhubung langsung dan rute ringkasan untuk satu RIP tidak berhubungan rute. Rute subnet yang hilang.
Langkah 7: Identifikasi dan berusaha untuk memperbaiki masalah
- Dari konfigurasi router, mengidentifikasi alasan untuk masalah yang Anda temukan pada Langkah 6. Jawaban : Router menggunakan RIP saat turut berpartisipasi dalam jaringan yg tdk berhubungan tanpa menentukan versi 2. RIP versi 1 adalah classful dan tidak melaporkan informasi subnet.
- Pada setiap router, menjalankan perintah untuk memperbaiki masalah ini. Perintah sampel dan keluaran untuk Utama ditampilkan.
- Kembali memeriksa tabel routing dengan hati-hati. Jelaskan mengapa, meskipun setiap router sekarang memiliki rute RIP, masih ada masalah dengan tabel. informasi subnet khusus masih hilang. Apa yang harus dilakukan untuk memperbaiki masalah? Matikan auto-summarization.
- Pada semua tiga router, berikan perintah untuk memperbaiki masalah ini. Contoh untuk Main ditampilkan. Utama (config-router) # no auto-summary
Langkah 8: Pastikan bahwa masalah tersebut telah dikoreksi
Lihat tabel routing. Rute harus dilaporkan sebagai ditampilkan untuk router utama.
Langkah 9: Refleksi
a. Kapan itu penting untuk melihat semua rute yang mungkin dalam tabel routing?
Jawaban : selama pemecahan masalah, atau ketika menangkap sepenuhnya berfungsi jaringan sebagai dasar.
RIP versi 2 mendukung VLSM, tapi berubah ke versi 2 tidak sepenuhnya menyelesaikan masalah. Mengapa? Jawaban: Apakah versi 1 atau versi 2, RIP masih merupakan protokol distance vector, dan protokol distance vector default ke summarization otomatis.
a. Kapan itu penting untuk melihat semua rute yang mungkin dalam tabel routing?
Jawaban : selama pemecahan masalah, atau ketika menangkap sepenuhnya berfungsi jaringan sebagai dasar.